A recent study has shown that chronic inflammation is linked to 60% of all deaths. It is a serious issue that is seemingly flying under most people’s radar. However, as health practitioners for over 20 years, we wanted to do our part in bringing awareness to this situation.
That is why Head Chiropractor Martin, and resident Nutritionist Laila, sat down to talk about what Chronic Inflammation is, why it is a problem and what you can do about it. (Some answers edited for brevity).
1. What is Inflammation?
Martin – Inflammation is an important part of the body’s response to any injury or infection. It is the start of a physiologic process that will repair trauma or fight off infection from viruses or bacteria. An acute or new inflammatory response is normal and necessary. Problems arise when the inflammatory process carries on unchecked for a prolonged period. The components of inflammation will wander around looking for things to ‘attack’ and could start targeting healthy tissues.
2. Where Does Inflammation Occur in the Body?
Martin – Inflammation can occur anywhere in the body, both internally and externally. Any area perceived to be damaged or infected will elicit the appropriate inflammatory response.

3. What are the Causes of Inflammation?
Martin – Trauma and infection are the most common causes of inflammation. In an acute situation, chemicals known as cytokines are released by the damaged tissues. These will cause blood vessels to dilate, increasing blood flow to an area. This response will bring in the body’s immune cells, hormones and nutrients to repair the problem.
Laila – There are also cases of autoimmune disorders where the body attacks itself, such as irritable bowel disease or Type I diabetes. However, smoking, obesity, alcohol and sustained stress also cause inflammation. Nicotine activates certain white blood cells that release molecules that lead to increased inflammation, heavy alcohol consumption can lead to ‘leaky gut’ and encourage widespread inflammation, some research has shown that overeating increases the immune response, and prolonged stress increases levels of cortisol in the body.

4. What are the Negative Effects of Inflammation?
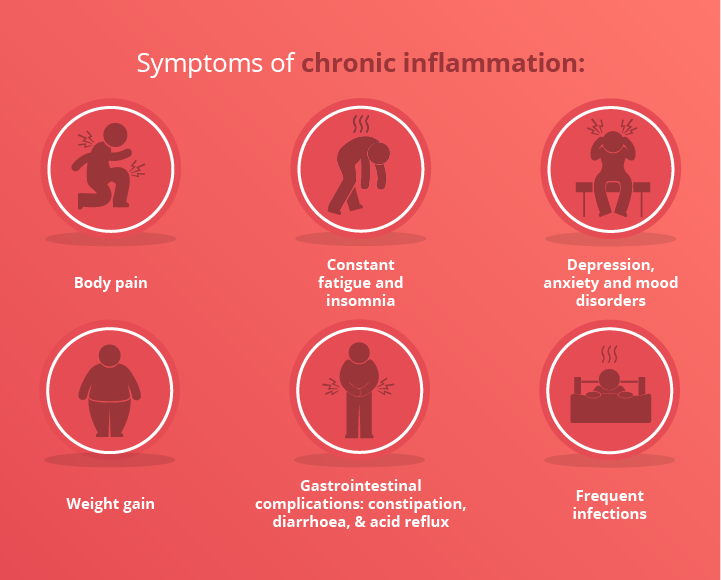
Martin – If an acute (new) inflammation persists beyond the normal healing mechanism time frame, it becomes chronic (old). Chronic inflammation can have long term and whole-body effects. Persistent inflammation causes a steady, low-level inflammation over a large area without a specific or controlled purpose. It is signalled by a rise in immune system markers that can be picked up by a blood test. The body perceives there is a threat and increases the white blood cells which essentially have no purpose. They may eventually start to attack internal organs or healthy tissues and cells. Prolonged inflammation can contribute to the development of diseases eg heart disease and strokes. In addition, chronic inflammation has been associated with damaging DNA which in turn could lead to some forms of cancer according to the National Cancer Institute.
Laila – As per Martin’s response – chronic inflammation eventually damages cells, tissues and organs and can lead to heart disease, Type II diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, obesity, asthma, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
5. Are There Any Positives of Inflammation?
Martin – Absolutely. In a normal, controlled environment, the inflammatory process is the first, essential step in a complex and brilliant mechanism that allows the body to heal itself from any injury or infection.
6. Does Diet Affect Inflammation?
Laila – Yes, positive and negatively. The positives are that if you regularly consume foods that reduce underlying inflammatory processes, this can be one of the best defences against chronic inflammation. On the opposite side of the spectrum, sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, trans fats, vegetable oils, seed oils, refined carbohydrates (such as sweets, bread, cakes, sugary drinks), alcohol and processed meats can cause inflammation as they cause negative metabolic effects in the body.
7. What Diet/Food can Reduce Inflammation?
Laila – Classic anti-inflammatory foods include berries, cherries, oranges, oily fish, extra virgin olive oil, peppers, chillies, avocados, green leafy vegetables, tomatoes, garlic, green tea and certain spices – turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, black pepper and cayenne.
8. Does Exercise Affect Inflammation?
Martin – Yes! Any strenuous activity has the capacity to evoke an inflammatory response within the body. This typically happens whenever forces applied to the body or to the connective tissues exceed the biomechanical or metabolic limits of that individual. This can result in micro or macro damage to those areas which would be the cause of post-exercise pain or Delayed Onset of Muscle Stiffness (DOMS). However, importantly this event leads to an important process called ‘adaption’ which allows the ‘injured tissue’ to heal allowing for a strengthening of that tissue. This enables a person to improve both structurally and physiologically, allowing for improvement in future performance.
9. What Exercise/Exercises/Practices Reduce Inflammation?
Martin – I think here it is important to distinguish between acute and chronic inflammation again. The above question is more pertinent for Chronic Inflammation and would involve healthy lifestyle choices. Move regularly to avoid functional imbalances. Avoid highly processed foods with ingredients you can’t pronounce. Drink water appropriately and sleep well. Healthy lifestyle choices create a stronger body that can tolerate the stresses that lead to chronic inflammation.
10. What Lifestyle Choices can Help Tackle Inflammation?
Laila – Eat a minimally processed and varied Mediterranean-style diet that takes into consideration any personal health issues. Consume fermented products for their probiotic properties such as kefir, Yakult, live yogurts, kombucha, kimchi and sauerkraut. Exercise regularly. Tackle stress. Get adequate sleep, so around 7 to 9 hours (too little or too much triggers inflammation).

11. What are the Benefits of Tackling Inflammation?
Martin – I think it boils down to leading a healthy lifestyle to create a stronger body that works better. Our bodies like to work within a healthy range. Too sedentary a lifestyle creates problems however going too far in the other direction e.g. over-exercising comes with its own set of problems. It is important to remember that a controlled inflammatory response makes our bodies stronger as it settles damage. However, too much inflammation for too long creates other health issues.
Laila – A healthier life, which means that you get to enjoy it more. Being ill is no fun and chronic diseases can put lots of restrictions on a person – more tablets, side effects, pain, limited mobility, potential to lose limbs or your life…it depends on the disease, but the impact of chronic inflammation is very serious.













